X chromosome inactivation is a crucial biological process that enables female mammals to balance their gene expression, given that they possess two X chromosomes while males have only one. This phenomenon not only highlights the complexities of cellular genetics but also serves as a foundational mechanism when exploring inherited genetic disorders, including Fragile X Syndrome and Rett Syndrome. As researchers delve deeper into the intricacies of X chromosome inactivation, innovative approaches like chromosomal therapy are emerging, promising potential advancements in treating these conditions. Understanding how this process works could unlock solutions for effectively managing genetic disorders that stem from mutations on the X chromosome. This introduction sets the stage for exploring the fascinating interplay between genetics, cellular mechanisms, and disease treatment.
Also referred to as X inactivation, this essential biological mechanism eliminates the potential overexpression of genes located on the X chromosome, significantly influencing development in females. The process is especially relevant when discussing chromosomal therapies aimed at rectifying the effects of genetic disorders such as Fragile X Syndrome and Rett Syndrome. By silencing one of the X chromosomes, females achieve a genetic equilibrium similar to that of males, which brings intriguing insights into the field of cellular genetics. With advancements in research, the potential for therapeutic interventions that address mutations on the X chromosome becomes increasingly feasible. Thus, the dynamics of X inactivation not only fascinate geneticists but also inspire hope for those affected by hereditary conditions.
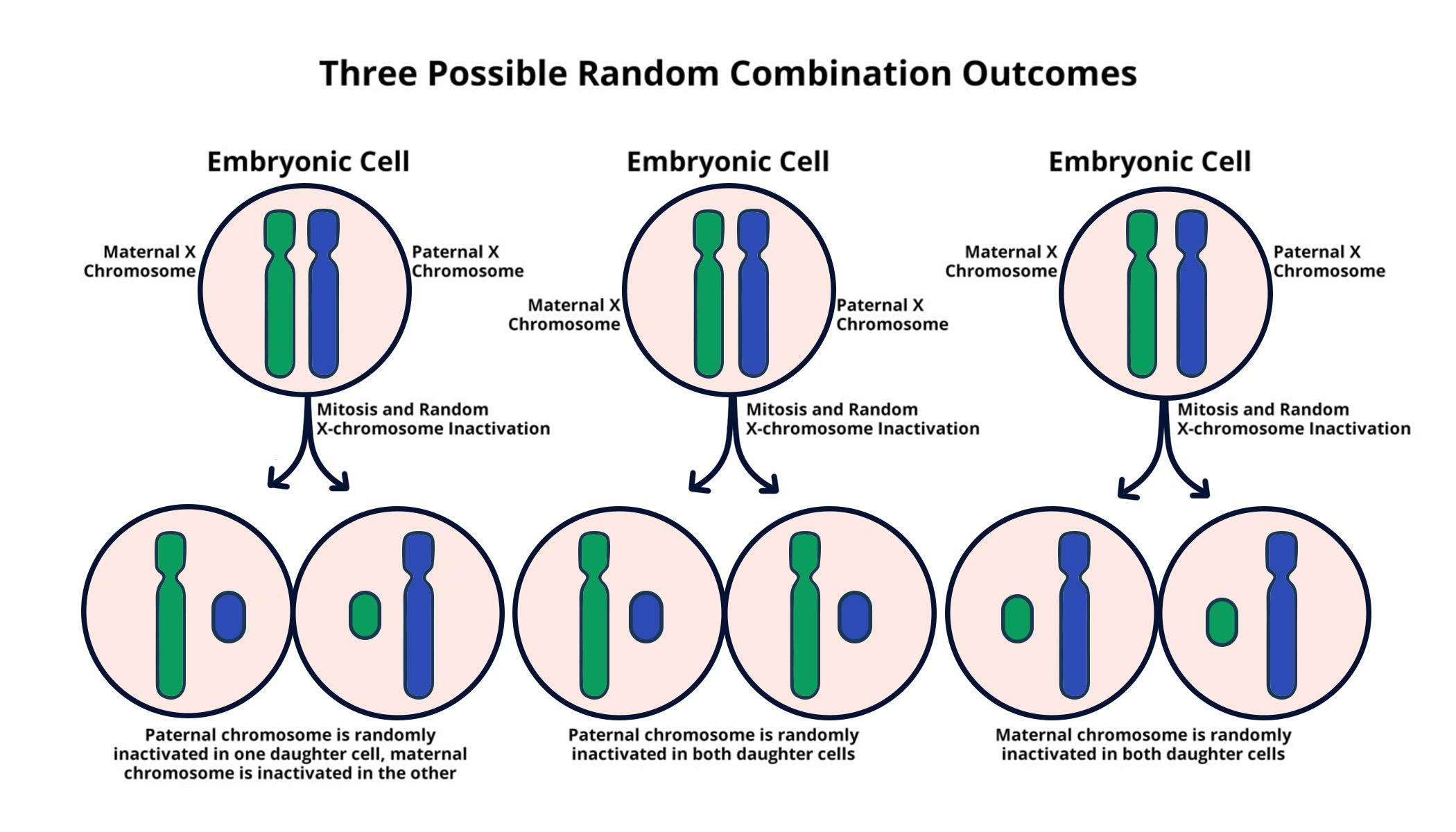
Understanding X Chromosome Inactivation
X chromosome inactivation is a crucial biological process that ensures females, who have two X chromosomes, do not express twice the amount of X-linked genes compared to males, who have only one X chromosome. This phenomenon involves one of the X chromosomes being randomly chosen to be inactivated in each cell, ensuring that males and females have similar levels of gene expression. Researchers like Jeannie T. Lee have been exploring the mechanisms behind this silencing process for years, revealing insights into why and how this complex system operates within human cells. Her recent findings suggest that a gelatinous substance plays a pivotal role in forming the necessary structure for this silencing, providing a more comprehensive understanding of cellular genetics and gene expression regulation.
The implications of understanding X chromosome inactivation extend beyond basic biological curiosity. This mechanism is not just important for cellular biology; it has enormous potential in medical research, especially concerning genetic disorders linked to the X chromosome. Disorders such as Fragile X Syndrome and Rett Syndrome are caused by mutations on the X chromosome, and insights into how inactivation works could lead to innovative therapies aimed at reactivating these silenced genes, offering hope to many affected individuals and families.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is X chromosome inactivation and why is it important in genetic disorders?
X chromosome inactivation (XCI) is a crucial biological process where one of the two X chromosomes in female cells is silenced to prevent the overexpression of X-linked genes. This mechanism is essential because it helps maintain genetic balance between the sexes, especially in the context of genetic disorders like Fragile X Syndrome and Rett Syndrome, where mutations can occur on the X chromosome. Understanding XCI can lead to novel therapies for these disorders.
How does X chromosome inactivation relate to Fragile X Syndrome?
Fragile X Syndrome is a genetic disorder caused by mutations on the X chromosome. During X chromosome inactivation, one X chromosome in females becomes inactive, which can trap the healthy gene and render it unusable. Research into therapy targeting XCI aims to unsilence these inactivated X chromosomes, potentially allowing expression of healthy genes and providing relief for those affected by Fragile X Syndrome.
What role does Xist play in X chromosome inactivation?
Xist is a crucial RNA molecule involved in X chromosome inactivation. It is produced from the X chromosome and alters the properties of a gelatinous substance surrounding the chromosomes, facilitating the silencing of one X chromosome in females. Understanding the function of Xist is key in developing treatments for genetic disorders, including Rett Syndrome, caused by mutations on the X chromosome.
Can chromosomal therapy impact X chromosome inactivation in patients with genetic disorders?
Yes, chromosomal therapy holds potential for impacting X chromosome inactivation. By targeting the mechanism of XCI, researchers aim to reactivate inactivated X chromosomes, which may allow healthy genes to function. This approach could lead to breakthroughs in treating genetic disorders like Fragile X Syndrome and Rett Syndrome, where normal gene function is critical for patient health.
What are the implications of unsilencing inactivated X chromosomes for diseases like Rett Syndrome?
Unsilencing inactivated X chromosomes may provide significant therapeutic benefits for diseases like Rett Syndrome. By reactivating the healthy X chromosome in females, researchers hope to restore proper gene function and alleviate symptoms associated with this neurodevelopmental disorder. This targeted approach may offer a novel treatment pathway with fewer side effects, as it focuses on specific mutated genes without affecting healthy ones.
What challenges exist in understanding X chromosome inactivation and its effects on genetic disorders?
Understanding X chromosome inactivation presents several challenges, particularly in deciphering how silencing occurs without affecting healthy genes. Research continues to explore why unsilencing can restore function to mutated genes in disorders like Fragile X Syndrome while sparing unaffected genes. This knowledge is crucial for developing effective therapies and unraveling the complexities of cellular genetics.
How does cellular genetics relate to X chromosome inactivation and therapeutic developments?
Cellular genetics examines the role of genes and chromosomes in cell function. Understanding X chromosome inactivation is fundamental to cellular genetics, especially concerning therapeutic developments for conditions such as Fragile X Syndrome and Rett Syndrome. By manipulating cellular mechanisms that control XCI, researchers are paving the way toward innovative treatments that could restore gene function and improve patient outcomes.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Understanding X Chromosome Inactivation | Females inactivate one X chromosome to balance gene dosage with males. |
| Role of Xist RNA | Xist alters the surrounding ‘Jell-O-like’ substance, aiding in silencing of the X chromosome. |
| Potential Treatment for Genetic Disorders | Research offers hope for treating Fragile X and Rett syndromes through unsilencing X-linked genes. |
| Clinical Applications | Methods are being developed for clinical trials to address X-linked genetic disorders. |
| Remaining Mysteries | Uncertainty remains about why only mutated genes are affected while healthy genes largely remain untouched. |
Summary
X chromosome inactivation is a crucial biological process that enables females to balance gene expression between sexes. This intricate mechanism involves the inactivation of one of the two X chromosomes in females, a process methodically studied by researchers like Jeannie T. Lee. The innovative findings regarding Xist RNA and its interactions with the chromosomal environment mark significant progress toward developing targeted therapies for genetic disorders linked to mutations on the X chromosome, such as Fragile X and Rett syndromes. With ongoing research, the clinical applications of these insights could profoundly impact treatment strategies, allowing for the possibility of unsilencing critical genes and offering new hope for affected individuals.
Comments are closed, but trackbacks and pingbacks are open.