Tropical forests play a crucial role in the fight against climate change, acting as vital carbon storage forests that help regulate the Earth’s atmosphere. However, climate change effects pose a significant threat to these ecosystems, particularly in terms of forest canopy health. Recent studies leveraging NASA GEDI technology reveal alarming insights into how these rich environments are impacted by factors such as heat and drought, emphasizing the urgent need for tropical forest assessment. The height of the forest canopy serves as a key indicator of ecosystem productivity and health, highlighting the delicate balance that sustains biodiversity. Protecting these tropical forests is not merely an environmental concern; it is essential for global climate stability and mitigating the adverse impacts of climate change.
Rainforests are often referred to as the planet’s lungs due to their unparalleled capacity for carbon storage and oxygen production. Yet, these lush landscapes face unprecedented challenges from global warming and changing climatic conditions. Understanding how these unique ecosystems respond to environmental stressors is critical not only for conservation but also for maintaining the delicate balance within our biosphere. Innovative methods, such as LiDAR technology from NASA, allow researchers to gain deeper insights into the structure and health of these vital habitats. Effectively preserving rainforest ecosystems is integral to combating the multifaceted threats posed by climate change.
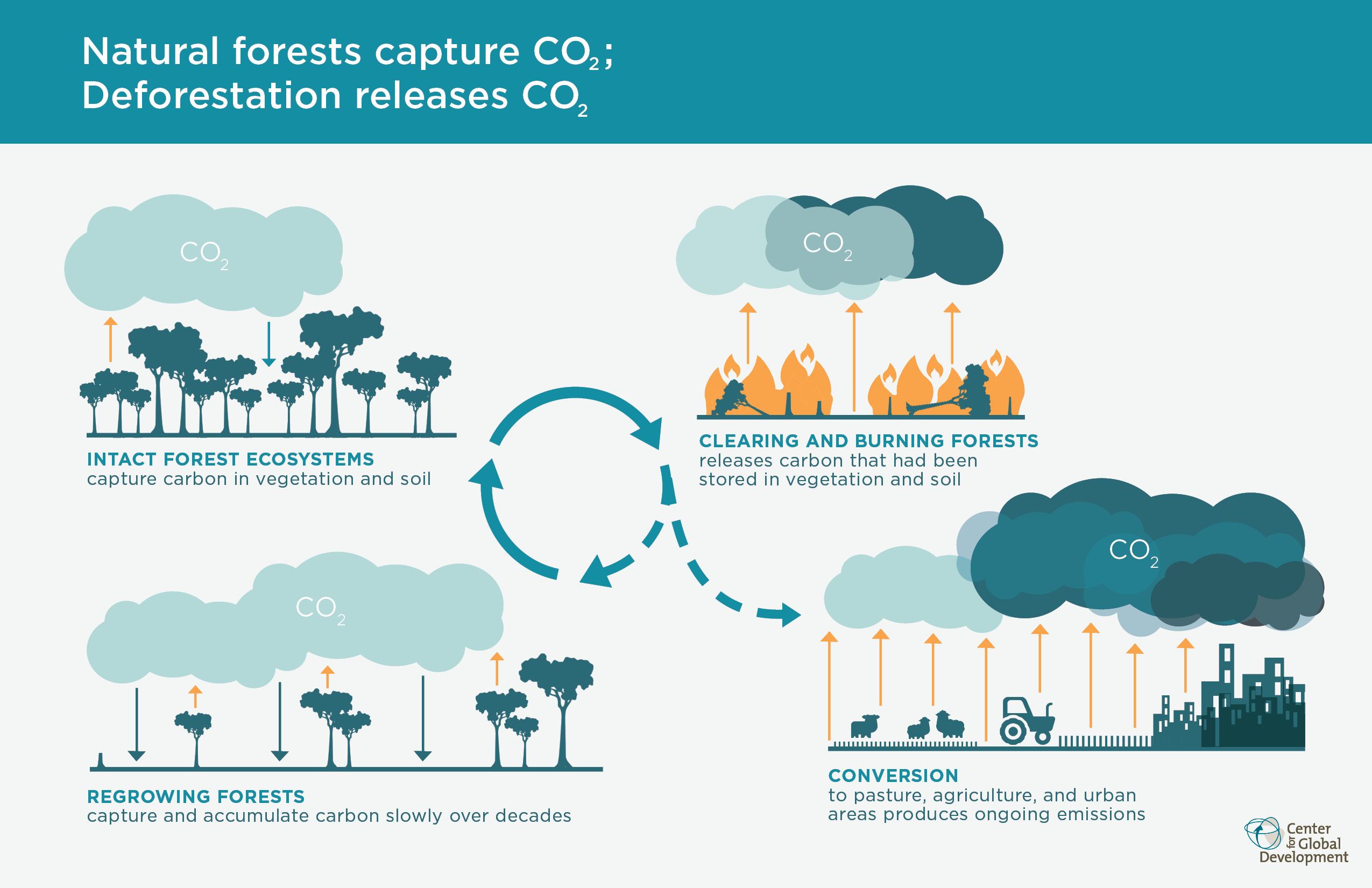
Understanding the Role of Tropical Forests in Climate Change
Tropical forests, often termed as the ‘lungs of the Earth’, play a crucial role in regulating the global climate. Through their extensive canopies, these forests not only store vast amounts of carbon but also influence local weather patterns. As climate change accelerates, the health of tropical forests is paramount in mitigating the adverse effects of climate change, such as increased temperatures and shifting rainfall patterns. Recognizing the vital functions of these ecosystems can help inform policy decisions aimed at preserving their integrity.
The ongoing study utilizing NASA’s GEDI technology highlights the intricate relationship between climate change and forest health. With the ability to assess the canopy height and its variations across different regions, scientists are uncovering how factors like drought and heat waves impact these critical ecosystems. Introducing advanced monitoring technologies allows for a deeper understanding of these dynamics, which is essential for formulating effective strategies to combat climate change.
The findings show that tropical forests are not just biodiversity hotspots but are integral to carbon dioxide absorption and storage. This capability makes them key players in the fight against climate change. By understanding the factors that affect canopy height, researchers can better estimate carbon storage potential and the overall health of these forests. Hence, preserving tropical forests can significantly contribute to global carbon reduction efforts.
Furthermore, as climate models predict longer dry seasons, especially in areas such as the southern Amazon, monitoring these changes through state-of-the-art technology becomes even more crucial. It is here that governments and organizations are called to action to implement protective measures. The science illustrates a dire need for initiatives that promote the sustainability of tropical forests, ensuring they continue to serve their essential ecosystem functions.
The Importance of Forest Canopy Health for Ecosystem Integrity
The health of the forest canopy is a key indicator of ecosystem productivity and overall forest vitality. A taller canopy not only signifies higher carbon storage but also enhances biodiversity by providing various habitats. As highlighted in the recent study, the forest canopy can buffer microclimatic conditions, which is especially important during heat waves, ultimately maintaining a stable environment for numerous species. By closely monitoring canopy health, researchers can gather vital data regarding ecosystem stability and resilience.
Tropical forest canopies are influenced by multiple environmental factors, including climate, topography, and soil properties. The research utilizing NASA’s GEDI technology indicates that a significant proportion of the difference in canopy height is attributable to these drivers. Understanding these variables is essential as they influence how these forests respond to climate variations. This knowledge allows for targeted conservation efforts that can help maintain the integrity of these critical habitats.
As climate change progresses, maintaining forest canopy health is vital for safeguarding not just the local wildlife but also the larger ecological balance. While varying conditions may prompt different responses from forest canopies, the overarching trend shows a concerning decline in health in many areas, particularly with protracted dry seasons becoming a common threat. Therefore, continuous monitoring and assessment of canopy health stand as a pillar for long-term conservation strategies.
Moving forward, researchers must focus on the implications of canopy health in the face of climate change. It is imperative to prioritize areas at risk and develop conservation strategies that can mitigate these impacts. The research reinforces that as the canopy health deteriorates, so too does the forest’s capacity to store carbon, exacerbating the issues at hand with climate change.
Technological Innovations in Tropical Forest Assessment
The advent of NASA’s Global Ecosystem Dynamics Investigation (GEDI) technology has revolutionized the way scientists assess tropical forests. By utilizing LiDAR technology from the International Space Station, researchers can now obtain high-resolution data on forest canopy heights across vast areas. This methodological leap enables a more comprehensive understanding of forest dynamics and health, paving the way for improved management practices. GEDI’s insights are invaluable for assessing the impacts of climate change on these ecosystems, as they allow scientists to observe changes that were previously difficult to measure.
The ability to visualize forest structures through laser measurements expands the horizons for forest research. This technology not only enhances the precision of tropical forest assessments but also helps identify significant variations in canopy height driven by environmental factors. With these insights, policymakers can make informed decisions regarding conservation priorities, focusing on areas most vulnerable to the effects of climate change. Such proactive measures are essential for ensuring that tropical forests continue to play their critical role in carbon storage and ecological balance.
In addition to improving assessment accuracy, GEDI technology also facilitates collaboration among researchers worldwide. By sharing datasets and findings, scientists can build a more thorough understanding of global forest health trends. This collaborative approach fosters a stronger response against climate change impacts, as data-driven decisions can be made considering regional variances and specific challenges faced in tropical woodland areas.
As research progresses, the integration of innovative technologies like GEDI promises to yield richer insights into tropical forest ecosystems. These advancements highlight the dynamic interplay between technology and environmental science, ensuring that the challenges posed by climate change are met with an informed and effective strategy.
Effects of Climate Change on Tropical Forests
Climate change poses a significant threat to the stability of tropical forests, which are already feeling the impact of increasing temperatures and changing rainfall patterns. The reliance on solely observational techniques has limitations, but with NASA’s GEDI technology, researchers can gain unprecedented insight into how these ecosystems respond to climatic alterations. By tracking forest canopy height variation, scientists are uncovering the direct effects of climate change, including prolonged dry seasons that contribute to reduced canopy height in regions like the southern Amazon.
Understanding these effects is critical not only for conservationists but also for policymakers who are designing climate action strategies. The study’s findings indicate that as dry seasons extend, the risk of reduced carbon storage capacity within these forests rises, which in turn affects global carbon levels. Tropical forests must be prioritized in climate change policies to ensure their survival and continued functionality in carbon sequestration.
The responses of tropical forests to climate challenges are not uniform; they vary regionally based on factors like topography and soil composition. The central Amazon, for example, demonstrates resilience due to its moist conditions, whereas other areas are significantly more vulnerable. This variation highlights the need for localized strategies in combating climate change, ensuring that interventions are tailored to specific forest types and their unique challenges.
Given these insights, ongoing research is vital. Scientists must continue to monitor how tropical forests adapt or succumb to climate shifts, utilizing advanced methodologies such as LiDAR technology. Protecting and preserving these vital ecosystems is not merely a local issue but a global imperative, underscoring the interconnectedness of climate action and forest conservation.
The Future of Tropical Forest Conservation and Policy Implications
As climate change continues to challenge the integrity of tropical forests, there is an urgent need for forward-thinking conservation policies. The insights gained from the use of NASA’s GEDI technology underscore the importance of identifying and prioritizing vulnerable areas that require immediate attention. Effective policy must incorporate scientific findings to allocate resources and protection measures to the most at-risk tropical forest regions. By framing conservation as not only an ecological necessity but also a critical component of climate change mitigation, we can garner greater public and governmental support.
Furthermore, integrating the knowledge of forest canopy health into forest management practices can yield substantial benefits in preserving biodiversity and enhancing carbon storage capacities. As the research indicates, a healthier canopy leads to a more robust ecosystem capable of withstanding climate fluctuations. Therefore, creating management frameworks that emphasize canopy health and ecosystem integrity should be front and center in global and local conservation strategies.
The path towards effective tropical forest conservation must also consider the socio-economic dimensions, engaging local communities in sustainable practices and policies. Empowering local populations to participate in forest stewardship fosters a collaborative approach to conservation that benefits both the environment and regional livelihoods. Education and awareness campaigns can further enhance community involvement, ensuring that conservation becomes a shared priority.
In sum, the future of tropical forest conservation hinges on a science-based approach to policy-making that recognizes the critical importance of these ecosystems in the face of climate change. By incorporating advanced technologies, local engagement, and a commitment to preserving forest canopy health, we can move towards a sustainable future for both the planet and its diverse inhabitants.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does climate change affect tropical forests’ carbon storage capabilities?
Climate change significantly impacts the carbon storage capabilities of tropical forests by altering forest canopy health and structure. Prolonged droughts and temperature increases can lead to reduced canopy height, which is associated with lower carbon storage and decreased ecosystem productivity. Research utilizing NASA’s GEDI technology highlights that factors such as heat and soil conditions directly influence canopy health and carbon storage in these vital ecosystems.
What role does NASA GEDI play in assessing tropical forest health related to climate change?
NASA GEDI (Global Ecosystem Dynamics Investigation) plays a crucial role in assessing tropical forest health by utilizing advanced LiDAR technology to measure forest canopy height and structure. This satellite-based tool enables scientists to evaluate how climate change effects, including drought and heat, vary across different regions, providing essential data that informs global assessments of forest health and carbon sequestration potential.
Why is forest canopy height important in understanding climate change effects on tropical forests?
Forest canopy height is a critical metric in understanding climate change effects on tropical forests because it reflects the overall health and productivity of the forest. Taller canopies typically indicate healthier ecosystems with higher carbon storage capabilities. Studies have shown that variations in canopy height are primarily driven by environmental factors influenced by climate change, making it an essential indicator for assessing the impact of climate change on both biodiversity and carbon storage in tropical forests.
How can tropical forest assessments aid in climate change mitigation?
Tropical forest assessments, particularly those that measure canopy health and changes in structure, provide essential insights into the forests’ capacity for carbon storage and biodiversity conservation. By understanding the areas most affected by climate change, policymakers can prioritize these regions for protection and sustainable management, effectively contributing to global climate change mitigation efforts.
What environmental factors affect tropical forest canopy height as per recent studies?
Recent studies using NASA GEDI data indicate that canopy height in tropical forests is primarily influenced by environmental factors such as climate conditions, topography, soil properties, and solar radiation. Notably, the length of dry seasons is a critical driver for canopy height, particularly in vulnerable regions like the southern Amazon, highlighting the importance of understanding these variables in the context of climate change effects.
What implications does the study of climate change on tropical forests have for conservation policy?
The study of climate change impacts on tropical forests has significant implications for conservation policy. It underscores the urgency of protecting these ecosystems, which are key for carbon storage and biodiversity. By identifying vulnerable areas through forest assessments, policymakers can develop strategic conservation efforts and allocate resources to areas most susceptible to climate change, ensuring the preservation of tropical forests as critical components of our planet’s health.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Role of Tropical Forests | Considered ‘the lungs of the Earth’, important for carbon storage and ecosystem health. |
| Impact of Climate Change | Climate change adversely affects tropical forests, revealing vulnerabilities through NASA’s GEDI technology. |
| Height of Canopies | Canopy height is crucial for assessing forest health; influenced by factors like temperature and drought. |
| Regional Differences | Variations in canopy responses to climate change were observed across regions, notably in South America and Africa. |
| Policy Implications | Research aims to influence climate policies by highlighting vulnerable forest areas. |
Summary
Tropical forests climate change presents a significant concern for global biodiversity and carbon storage. As vital ecosystems, these forests face unprecedented challenges from prolonged dry seasons and rising temperatures, which can drastically reduce their canopy heights. Studies utilizing NASA’s GEDI technology have showcased the diverse impacts of climate change across various regions, emphasizing the necessity of protective measures and informed policy changes to sustain these critical environments for future generations.